Disease affecting the ret...
Disease affecting the retina retina is composed of multiple layers of thin, transparent neuronal tissue constructing the inner lining of the [...]
تقاطع شریعتی و بزرگراه همت، خیابان گل نبی غربی، پلاک 3
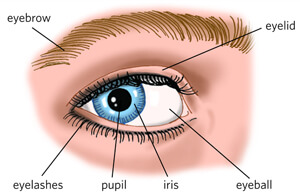
upper and lower eyelids open and close and they provide protection to the globe
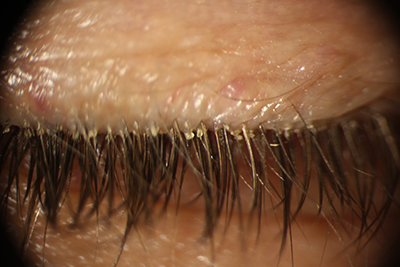
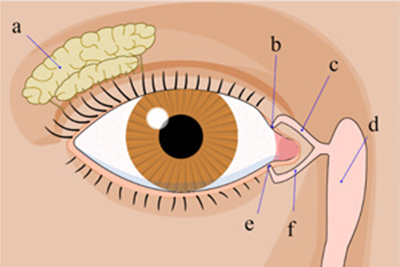
this condition is accompanied by ocular redness, burning sensation, tearing, and foreign-body sensation. Treatment consists of warm compress, eyelid hygiene, and topical and systemic medications.
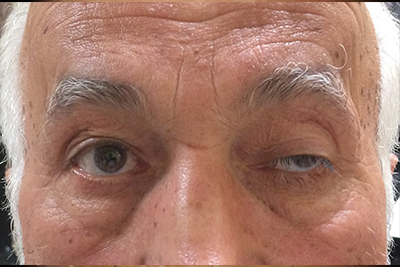
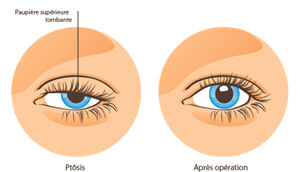
droopiness of the upper eyelid affecting one or both sides referred to as ptosis. Ptosis can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired (obtained later in life). Some of the presenting signs include asymmetry in palpebral fissure (opening of the eyes), decreased vision in the superior aspect of the visual field, amblyopia (in children), and headaches. Headaches are usually located in the forehead area due to excessive use of the forehead muscles to help raise the eyebrows and eyelids to compensate for the droopy lids; the treatment is often surgical.
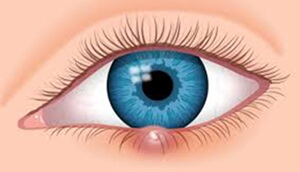
hordeolum is caused by the infection of the oil glands of the hair follicles and it usually presents itself as a red, painful mass. Treatment consists of warm compress, eyelid hygiene, and oral and topical antibiotics.
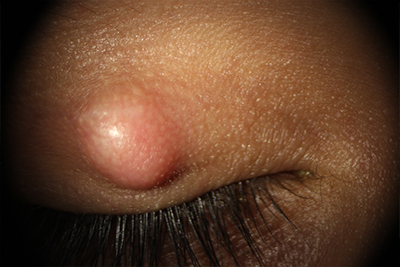
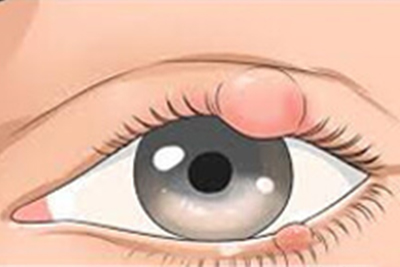
this is the inflammation of the meibomian glands (special oil glands at the margin of the eyelids). Treatment consists of warm compress, eyelid hygiene, oral and systemic medications, and surgical drainage is more severe cases.
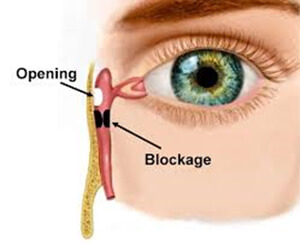
this condition is usually seen in 2-4% of infant causing epiphora (excessive tearing). In majority of the cases the underlying pathology is due to the presence of a thin membrane along the tear duct canal due to incomplete canalization. In some cases, however, this condition is due to a more serious anatomical malformation which is poorly responsive to therapy. Treatment chosen by the surgeon varies depending on the underlying etiology.