Presbyopia
presbyopia is the gradual decease in the ability of the eye to accommodate, and it is a normal part aging. Individuals [...]
تقاطع شریعتی و بزرگراه همت، خیابان گل نبی غربی، پلاک 3
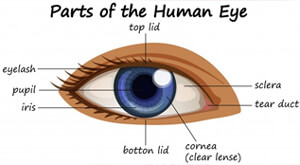
Cornea is the front most part of the globe consisting of an avascular transparent tissue that is continues at the limbus with the sclera.
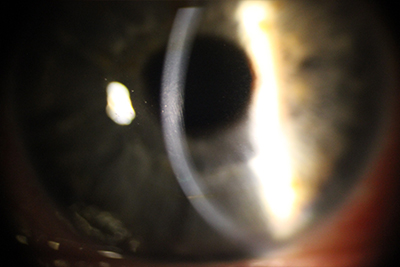
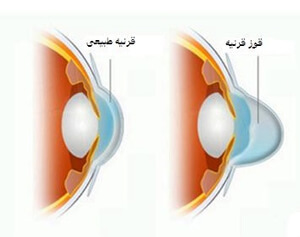
this progressive disease starts around the puberty and progresses until the middle ages that is often accompanied by a significant decrease in vision. In affected individuals, the center of the cornea becomes thin and bulgy as depicted in the picture. Patients are advised to refrain from rubbing their eyes as this may cause rapid progression of their condition. First line of therapy consists of glasses and contact lenses; in more severe cases, corneal transplant is often necessary to restore vision.
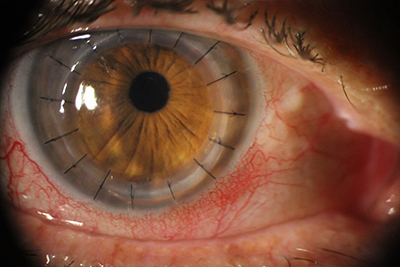
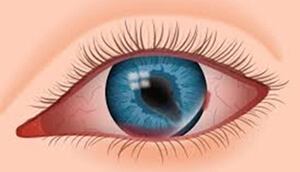
a corneal abrasion may take place as a result of trauma, contact lens wear, or foreign bodies. This is usually accompanied by severe pain which worsens upon blinking. The affected individuals suffer from pain, photophobia, and tearing. The treatment should be managed by an ophthalmologist only.

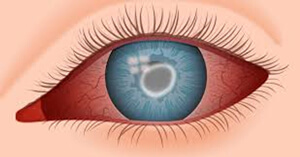
corneal ulcers present with varying degrees of severity and they are often accompanied by pain, redness, photophobia, foreign body sensation, and decreased vision. Treatment consists of frequent topical and oral antibiotics as well as surgery in more advanced cases.
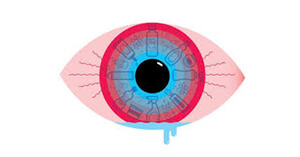
any chemical agent such as detergents, cosmetics, and corrosive substances (acid or base) can cause a chemical burn. The most important step in treatment of chemical burns of the cornea is early initiation of copious ocular irrigation.
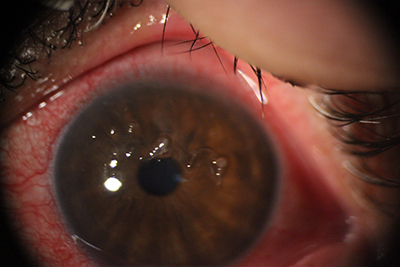

disturbance of the tear film due to deficiency of tear production or increase in tear evaporation leads to ocular surface damage and ocular discomfort, foreign body sensation, itching, burning and redness. Various medical and nonmedical treatment options may be undertaken to improve this condition. These include using humidifiers to moisten the air, avoiding dry, polluted, windy environments; oral and topical medications; and surgical closure of the punctums (tear drainage system of the eye).

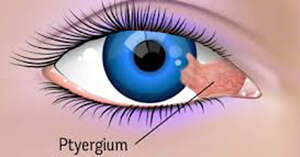
growth of the conjunctival tissue over the cornea is referred to as pterygium. It may causes burning, redness, foreign body sensation, and decreased vision. Treatment consists of protection of the eye from UV radiation by wearing UV-blocking sunglasses, eye drops, and surgery.
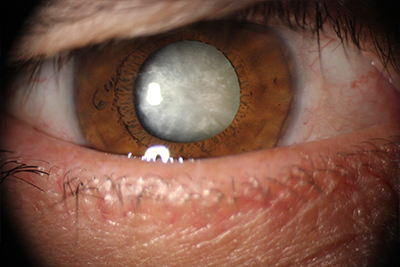

opacity of the crystalline lens leading to decreased vision is referred to as cataract. More than half of people over the age of 65 years old have significant cataract. Signs and symptoms include blurry vision, increase in near-sightedness, poor perception of previously identified colors, difficulty with night driving, double vision, and a rapid change in the prescription of glasses. Different types of cataract exist. They include congenital cataracts, senile cataracts, and traumatic cataracts. The treatment options vary from prescribing glasses to extraction of the cataract with implantation of an artificial lens via surgery.
glaucoma is an optic neuropathy accompanied by a gradual loss of vision and visual field due to an elevated intraocular pressure. In these patients, poor nourishment of the optic nerve leads to loss of vision.
